The nuts and bolts of Brain Based Learning
Are you familiar with how our brain works and its implications in the classroom? Though we may not know the details of our brain anatomy, it’s essential that we understand how it influences our behavior and learning. This article will explore the nuts and bolts of brain-based learning to maximize our students’ potential. From understanding the chemistry of stress and how it can hinder learning to discovering ways to motivate students. Plus, you’ll get some actionable strategies to empower your learners!

The Reptilian Brain
This is the lowest and oldest part of the brain, and we share it with all other animals. It evolved during the Triassic period and is connected to the spinal cord. Its main function is to guarantee survival. When in danger, it releases chemicals to face the “fight or flight” response. It also controls other functions to sustain life, such as heart rate, breathing, digestion, and sleeping.
In the class
A secure environment in the classroom will keep the reptilian brain at ease and it will promote effective learning. A stress-free class will help students to think reflexively rather than reflectively.
Tip: Playing classical or chill-out music in the background will help students feel relaxed and ready for learning.
To listen to the playlist I use with my own learners CLICK HERE!

The Mammalian Brain
It evolved after the reptilian brain during the Jurassic period, and it is located in the limbic system. The mammalian or emotional brain contains these important organs:
- Hypothalamus: for the automatic control of body functions such as digestion, body temperature, and blood pressure
- Hippocampus: for storing experience-based memories.
- Amygdala: For recognizing danger and for responding to this according to past experience
Under stress, the emotional brain hinders learning and downshifts to the reptilian brain to ensure survival. When the mammalian brain is in a positive and relaxed state it releases endorphins which trigger a powerful neurotransmitter called acetylcholine which favors learning.
In the class
Create a positive environment in the classroom, put up posters with uplifting phrases, smile, and show great enthusiasm for learning. Happiness is really contagious so if the teacher is happy students will be happy too!

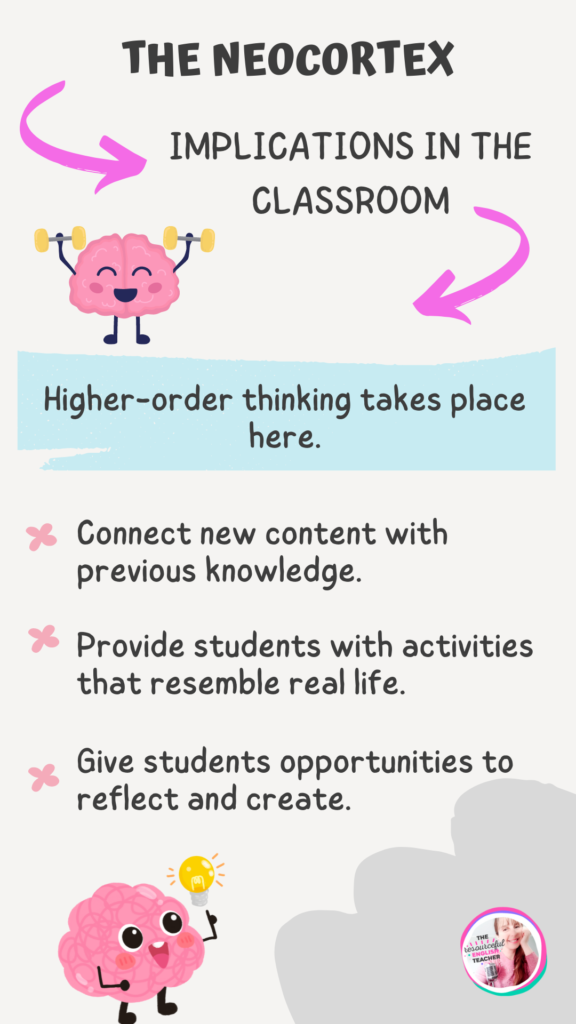
The Neocortex
With its tremendous amount of grey matter, the neocortex was added to the mammalian brain. It evolved with the first primates. It is also called the human brain, and its primary functions are: planning, creating, setting goals, speaking, regulating decision-making, and learning. Higher-order thinking takes place here.
In class
First of all, the brain will function properly only if it is appropriately fed and has reasonable hours of sleep. If those conditions are met then we can proceed to teach.
- What is taught should be relevant and significant in students’ lives. The brain learns best when it learns in a real-world context. Using activities similar to real life will enhance learning (projects, stories, field trips). Check out these bundles with Projects for your students! BUNDLE FOR PRIMARY SCHOOL STUDENTS. BUNDLE FOR SECONDARY SCHOOL STUDENTS.
- Help children to construct information instead of providing them with answers.
- Dividing content into smaller chunks helps to understand concepts better. The brain can retain up to seven bites of information. This can vary from human to human to 5-9 bites.
- Provide students with time to reflect and create.
- Reenergize your classroom with brief but meaningful brain breaks! These activities give students a chance to stretch their cognitive muscles, release some physical energy, and become more alert. Additionally, regular brain breaks help students to re-engage with the lesson material and keep classrooms energized. Download my favorite Brain Breaks for free HERE!
Our brain is one of the most amazing organs in our body, and understanding how it works is key to maximizing our students’ potential in the classroom. Applying the principles of brain-based learning can help us create a nurturing environment in which our students can thrive. We can do this by creating a secure environment, reducing stress, and providing relevant and meaningful learning experiences. We can help our students become empowered learners, capable of achieving their goals, both in and out of the classroom.
Take care,
Paula.